






|
 |
Plasma electronics laboratory
General Physics Inst., 38 Vavilova str.,
119991 Moscow, Russia
Tel: (095)135.6387.
Fax: (095)135.8011
Head: professor Pavel S. Strelkov
e-mail: strelkov@fpl.gpi.ru
|

|
Scientific directions:
- plasma relativistic microwave oscillator
- high-power microwave pulse shortening
- plasma relativistic microwave amplifier
Accelerator “TEREK-2”
500 keV, 10 kA, 30 ns
Head: Dr. Denis K. Ulyanov e-mail: dox@fpl.gpi.ru
Accelerator “TEREK-3”
700 keV, 5 kA, 1 mcs
Head: Dr. Oleg T. Loza e-mail: loza@fpl.gpi.ru
Accelerator “TEREK-3W”
700 keV, 30 kA, 100 ns
Head: A.V.Ponomarev e-mail: ponomarev@fpl.gpi.ru
High-power microwave sources:
features & advantages of “plasma” and “relativistic”.
Relativistic velocity of the electron beam excites waves in plasma with:
… phase velocity close to light speed. This alleviates extraction of microwaves from plasma into vacuum in wide frequency range.
… group velocity close to light speed. This provides low Q-factor of resonators and, hence, permits high power of microwaves.
Plasma
- …compensates electron beam space charge and (unlike vacuum electronics) permits to utilize electron currents exceeding the vacuum limiting current;
- …allows to tune microwave frequency
over a wide range by means of plasma density varying.
| Ref.:
|
M.V.Kuzelev, O.T.Loza, A.A.Rukhadze, P.S.Strelkov, A.G.Shkvarunets. "Plasma Relativistic Microwave Electronics". Plasma Physics Reports, Vol. 27, No. 8, 2001, pp. 669-691.
|

|
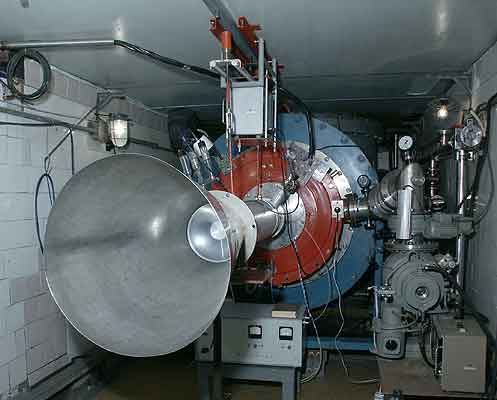
Cherenkov plasma maser (CPM)
|

|
|
Research is carried out since 1982. During this time:
- · Microwave power 500 MW with the efficiency 10%; registered using the microwave detector and the calorimeter.
Ref: M.Birau, et al. Proc. 23-th Int. Conf. On Phenomena in ionized gases. (ICPIG'97), Toulouse, July 17-22, 1997, vol. III, pp.46-47.
- Microwave frequency tuning: plasma may be reset during ~ 100 mcs
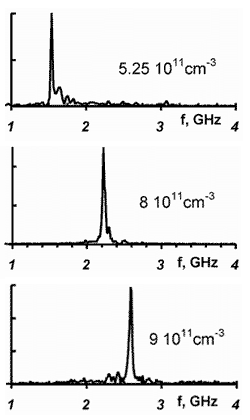
Figure 2. Narrow-band regime: spectrum of the CPM with different plasma concentrations at 50 MW power level.
- Microwave spectrum width of a single pulse may be broad
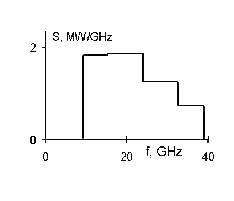
Figure 4. Broad-band regime: microwave spectrum of a 50-ns pulse. registered using the spectrometer.
- Microwave power and the pulse duration remain almost the same throughout the frequency range
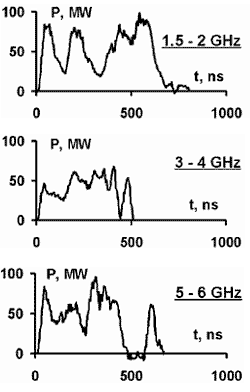
Figure 3. Waveforms of microwave pulse power in different frequency bands. Obtained using the microwave detector and the spectrometer.
- The theory has been developed, numerical model and simulation codes were designed, calculations were conducted
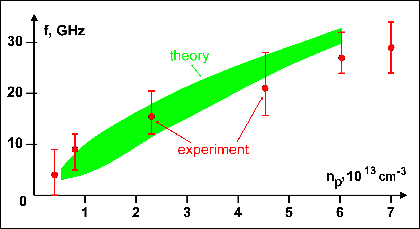
Figure 5. Microwave radiation frequency f vs plasma concentration np: theoretical predictions are in good accordance with experimental results. Microwave power ~
50 MW. Vertical lines represent measured microwave spectra.
| Ref.: |
P. S. Strelkov and D. K. Ul'yanov. "Emission Spectra of a Cherenkov Plasma Relativistic Maser Plasma Physics Reports", Vol. 26, No. 4, 2000, pp. 303-307.
|

|
Conferences:
15th International Conference on High-Power Particle Beams (Beams'2004), St. Petersburg, July 18-23, 2004
|
O. T. Loza. "On the mechanism of HPM pulse shortening in oscillators driven by relativistic electron beams"
|

|
|
A. V. Ponomarev, P. S. Strelkov. "Experimental Investigations of Cherenkov Plasma Amplifier"
|

|
|
I. L. Bogdankevich, P. S. Strelkov, V. P. Tarakanov, D. K. Ulyanov. "The influences of reflected electrons on the REB potential and on the energy distribution function of the REB electrons"
|

|
Papers:
|
A. G. Shkvarunets. "A broadband microwave calorimeter of large cross section". Instruments and Experimental Techniques, vol. 39, No. 4, 1996, pp. 535-538.
|

|
|
O.T.Loza, A.V.Ponomarev, P.S.Strelkov, et al. "Source of an annular controlled-radius plasma for a plasma relativistic microwave oscillator". Plasma Physics Reports, vol.23, No.3, pp.201-208, 1997.
|

|
|
I. L. Bogdankevich, P. S. Strelkov, V. P. Tarakanov, et al. "A calorimetric spectrometer measuring single pulses of relativistic microwave generators". Instruments and Experimental Techniques, vol. 43, No. 1, 2000, pp. 82-87.
|

|
|
P. S. Strelkov and D. K. Ul'yanov. "Emission Spectra of a Cherenkov Plasma Relativistic Maser" Plasma Physics Reports, Vol. 26, No. 4, 2000, pp. 303-307.
|

|
|
I. L. Bogdankevich, I. E. Ivanov, O. T. Loza, et al. "Fine Structure of the Emission Spectra of a Relativistic Cherenkov Plasma Maser". Plasma Physics Reports, Vol. 28, No. 8, 2002, pp. 690-698.
|

|
|
M.V.Kuzelev, O.T.Loza, A.A.Rukhadze, P.S.Strelkov, A.G.Shkvarunets. "Plasma Relativistic Microwave Electronics". Plasma Physics Reports, Vol. 27, No. 8, 2001, pp. 669-691.
|

|
|
A. V. Ponomarev, P. S. Strelkov, and A. G. Shkvarunets. Tunable Plasma Relativistic Microwave Amplifier. Plasma Physics Reports, vol. 26, No. 7, 2000, pp. 592–597.
|

|
|
|
 |











